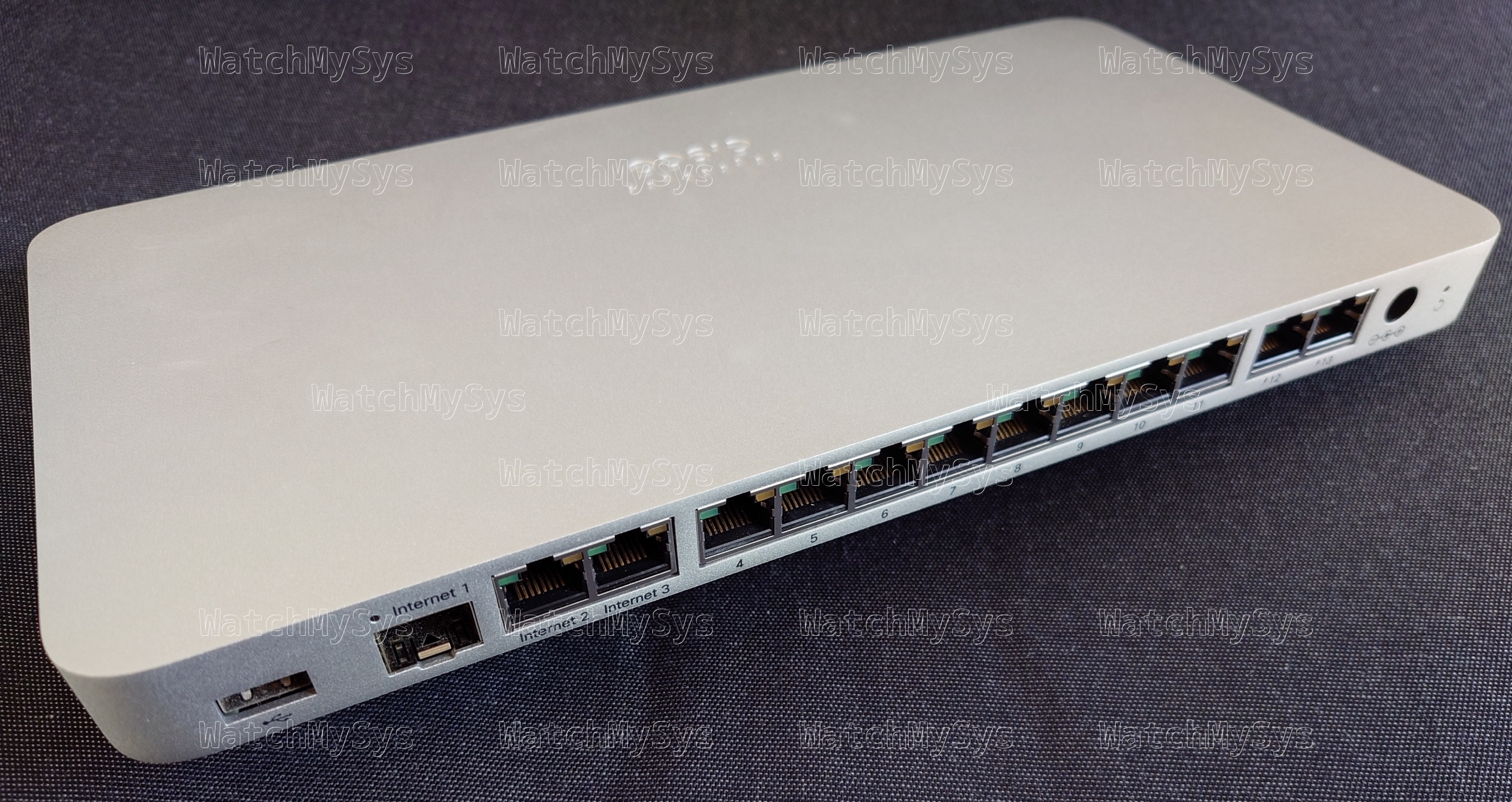
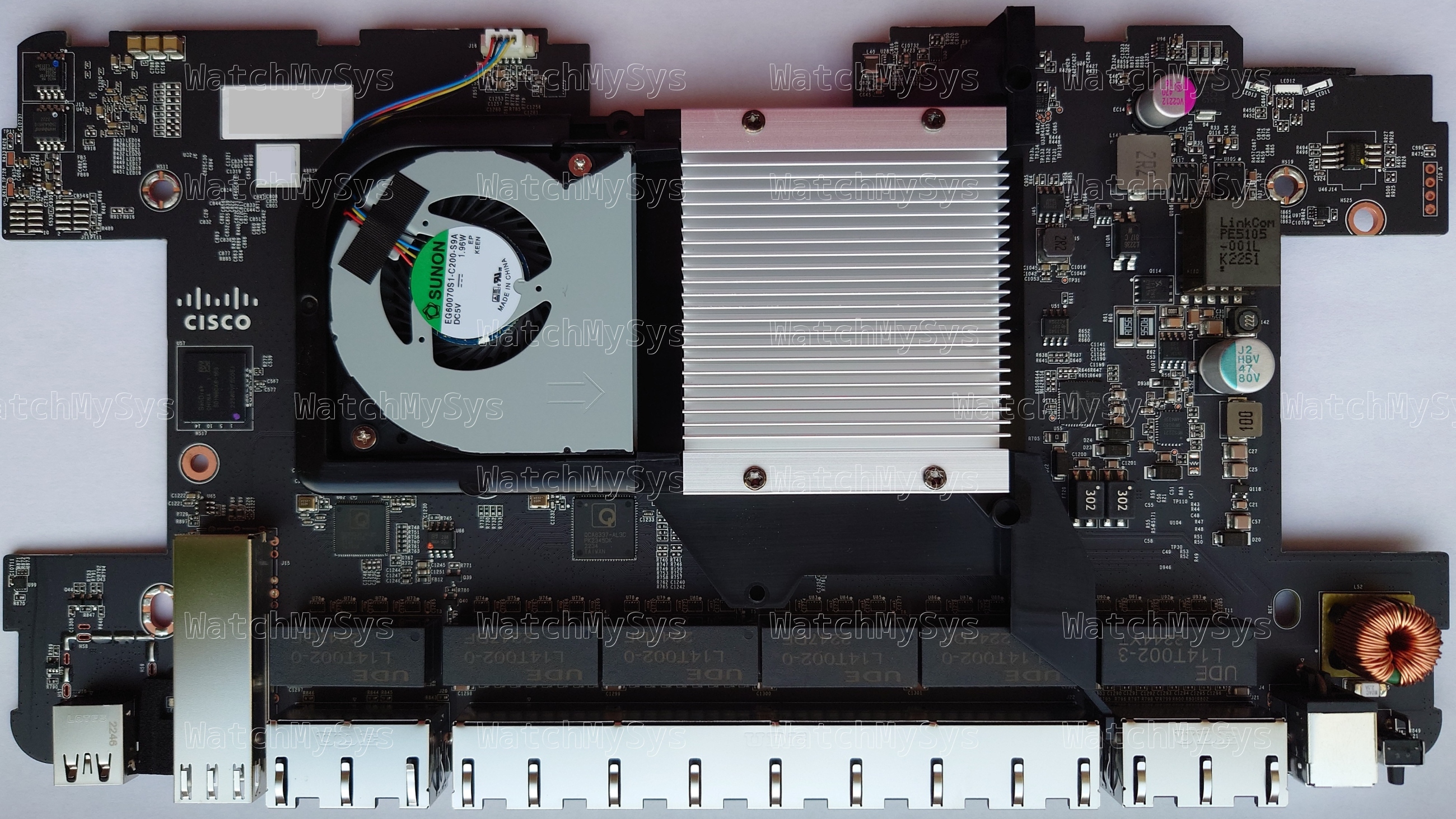
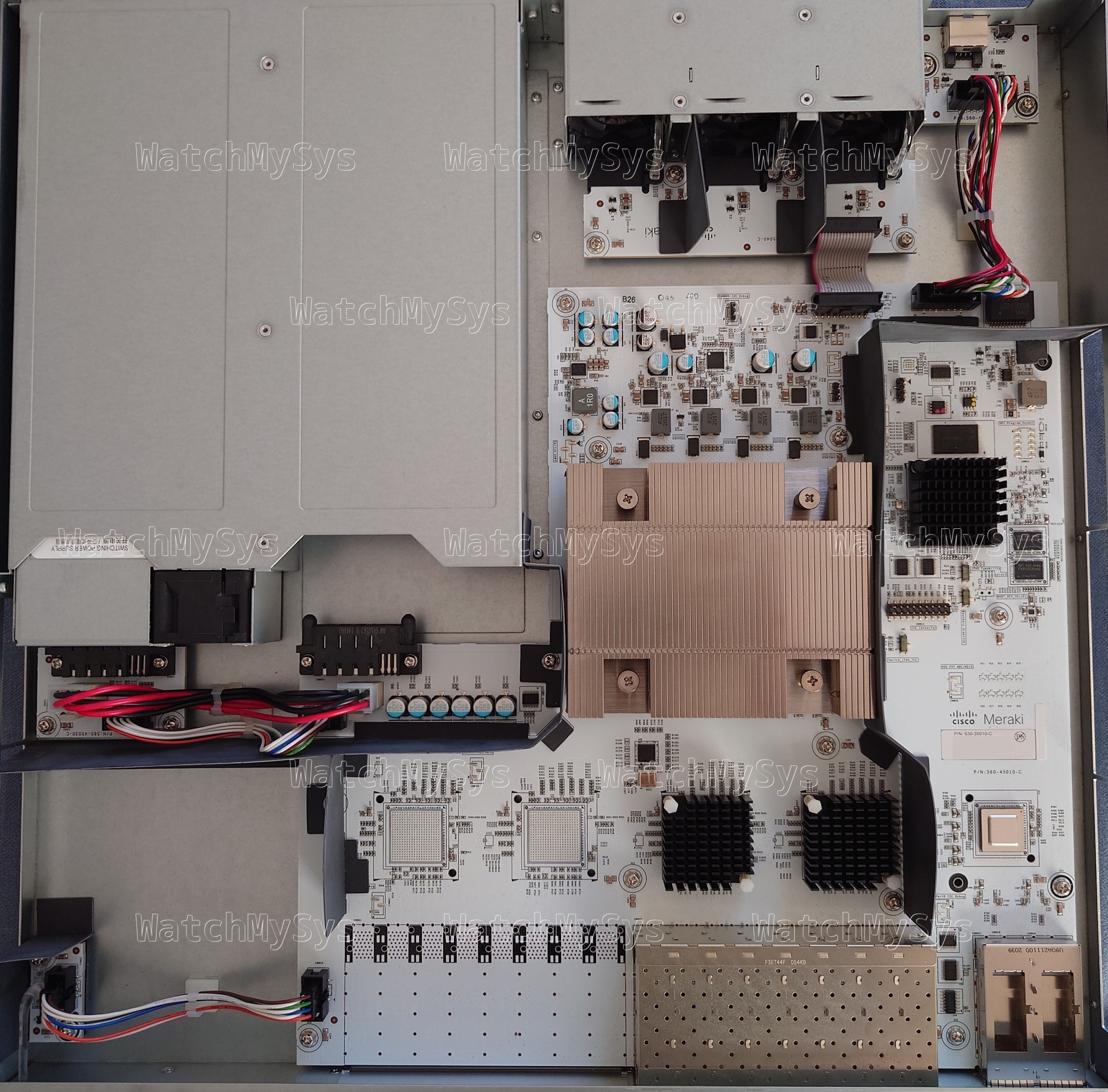
The Meraki MS410 series switches (codename “Wolfcastle”) offer 16 or 32 1000Mbit SFP ports, 10G SFP+ uplink ports, two HiGig2 (QSFP+) stacking ports, and a Gigabit Ethernet management port.
The MS410 was discontinued in September 2024, and is too old to support secure boot.
Here is a quick summary of the MS410-16 specs:
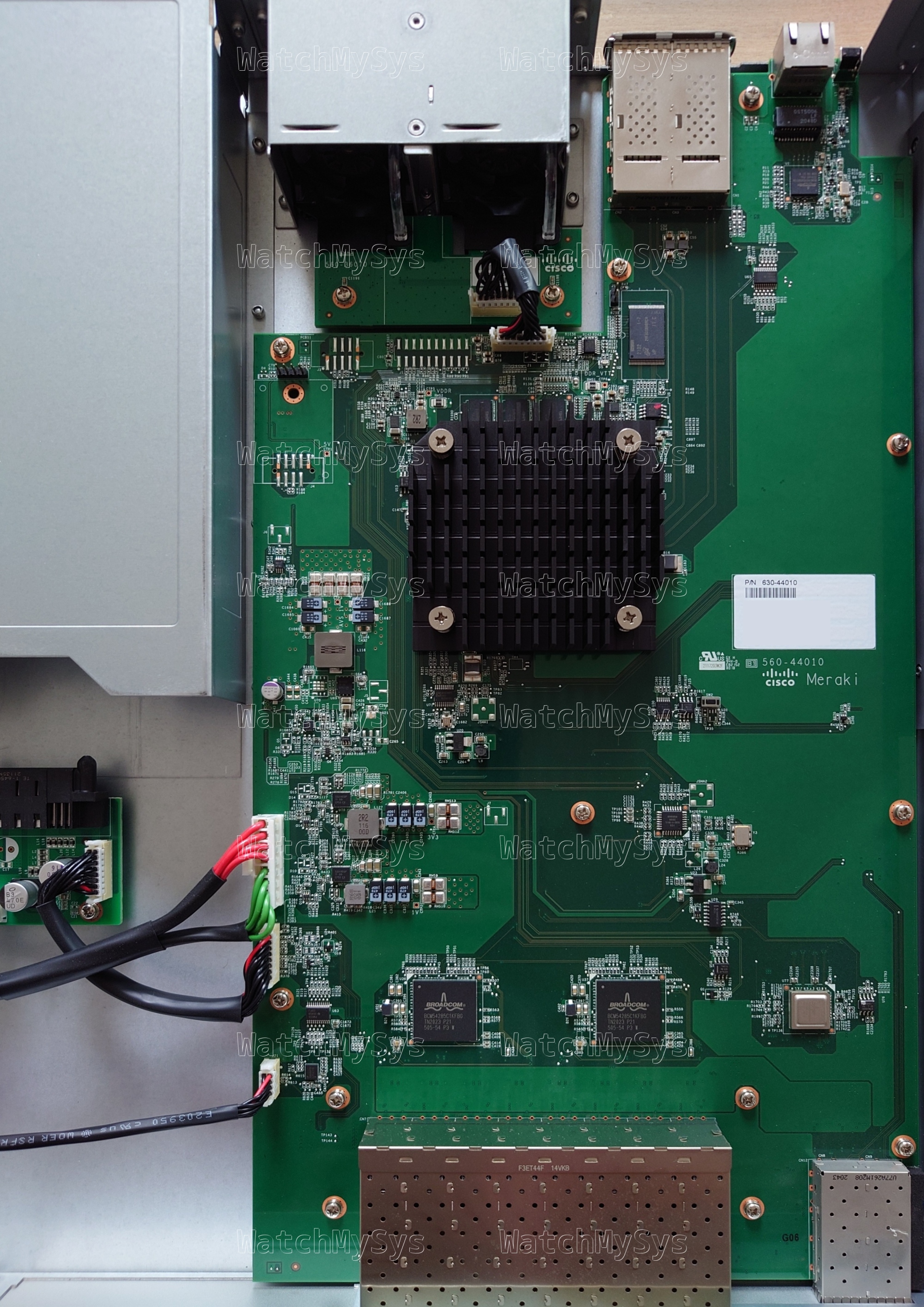
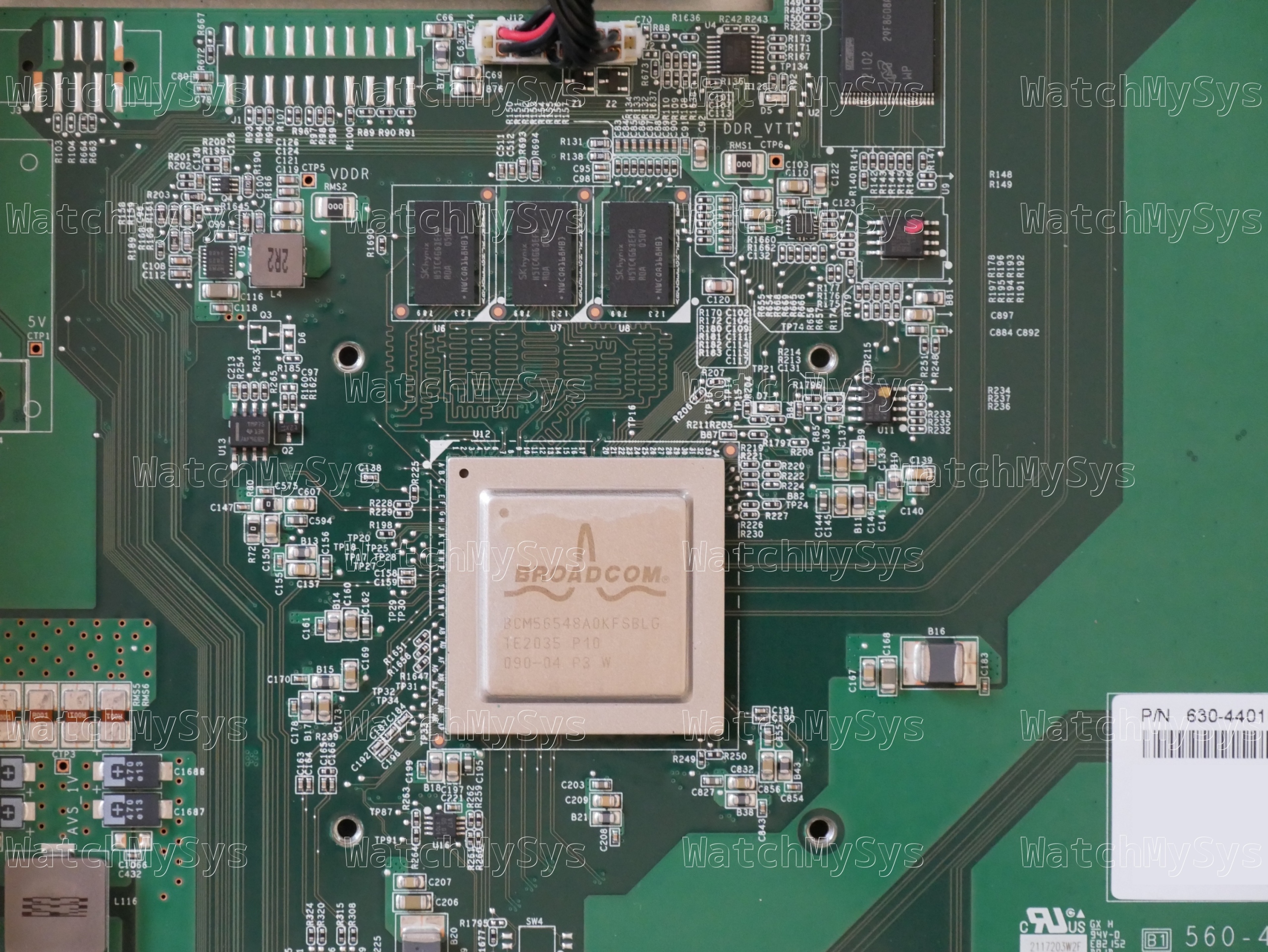
- Broadcom BCM56548 (A0) ASIC
- Broadcom BCM54285C1KFBG QSGMII Octal Gigabit PHY
- Broadcom BCM82752A3KFSBG PHY
- 16MB of SPI flash (MX25L12805D)
- 1GB DDR3 RAM (SK Hynix H5TC4G63EFR; soldered, ECC, PDF datasheet)
- 1024MB NAND flash (Micron MT29F8G08ABACAWP; PDF datasheet)
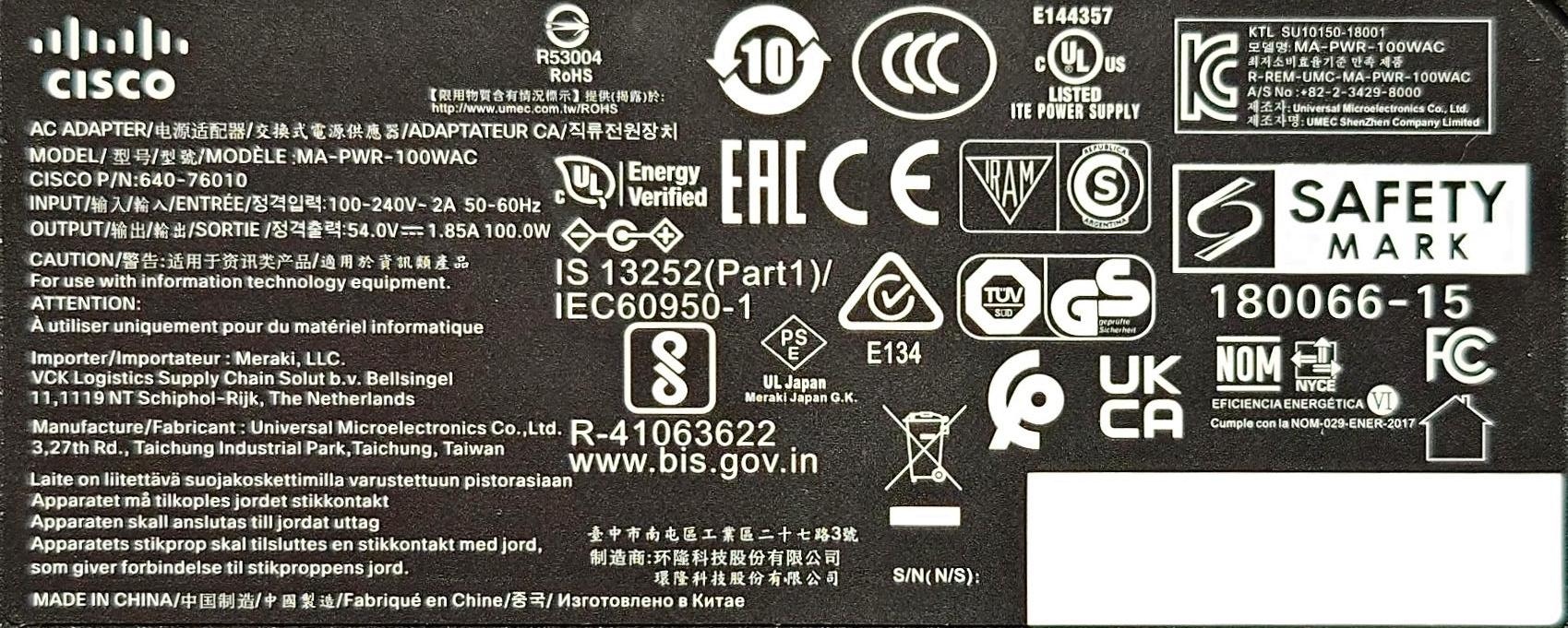
- MA-PWR-250WAC (identical to PWR-C2-250WAC)
The UART header in the MS410-16 is J2 and follows the standard Meraki UART pinout (1: 3.3V Vcc, 2: Tx, 3: Rx, 4: GND) at 115200 baud.
Unlike the MS420-24 and MS425-16, the MS410-16 is not a cut-down version of the MS410-32 with fewer PHYs and SFP cages. As the BCM56548 supports only 24 ports, we can speculate that the MS410-32 may use two stacked internally.
The MS410 is quite rare on the used market, and I am not aware of any MS410-32 available for a reasonable price. If you have one and are interested in donating it, claimed status does not matter, please reach out!
Unlike the MS350, MS420, and MS425, the management plane in the MS410 is not a discrete CPU but is integrated into the StrataXGS ASIC, similar to the MS210/225/250 series. The MS410 runs the same firmware release (switch-arm) as the MS210/MS225/MS250 series.
As the CPU is integrated into the switch ASIC, there are no devices present on the PCI(e) bus.
The Broadcom SDK series implements the packet engine in userspace, using the GPL-licensed linux_kernel_bde and linux_user_bde kernel modules to interface with the ASIC. In the Meraki firmware, the packet engine is a component of the userspace click daemon, which loads the bcm_click shared object during click router initialisation.
The stock Meraki boot process uses U-Boot on SPI to load a “bootkernel” (also from SPI), which then initializes NAND and using kexec boots the main firmware. The firmware layout follows the standard Meraki practice of having A/B firmware images: bootkernel1, bootkernel2, part.safe, part.old.
The firmware layout on SPI is:
0x000000-0x100000 : "uboot" 0x100000-0x800000 : "bootkernel1" 0x800000-0xf00000 : "bootkernel2"
The MS410 design predates Cisco Aikido secure boot, and therefore the firmware is not signed. Unlike recent Meraki products, U-Boot on the MS410 is not compiled with ENV_IS_NOWHERE, as we can see from the bad CRC, using default environment line below:
Press Ctrl-C to run Shmoo ..... skipped Restoring Shmoo parameters from flash ..... done Running simple memory test ..... OK DeepSleep wakeup: ddr init bypassed 3 Enabling DDR ECC reporting clear_ddr: OK Enabling DDR ECC correction DDR Interface Ready DRAM: 1 GiB WARNING: Caches not enabled NAND: Micron MT29F8G08ABACA, blocks per lun: 1000 lun count: 1 256 KiB blocks, 4 KiB pages, 27B OOB, 8-bit NAND: chipsize 1024 MiB SF: Detected MX25L12805D with page size 64 KiB, total 16 MiB *** Warning - bad CRC, using default environment
By default no U-Boot environment is present on SPI NOR, so U-Boot uses the environment compiled into the binary, which has bootdelay=0 and thus you cannot interrupt the automatic boot.
However, if you create a valid environment at 0xc0000 with a positive bootdelay, then you can interrupt U-Boot and obtain a shell. 0xc0000 is the default offset for storing the U-Boot environment on this generation of Broadcom switching ASICs, which Meraki has not modified.
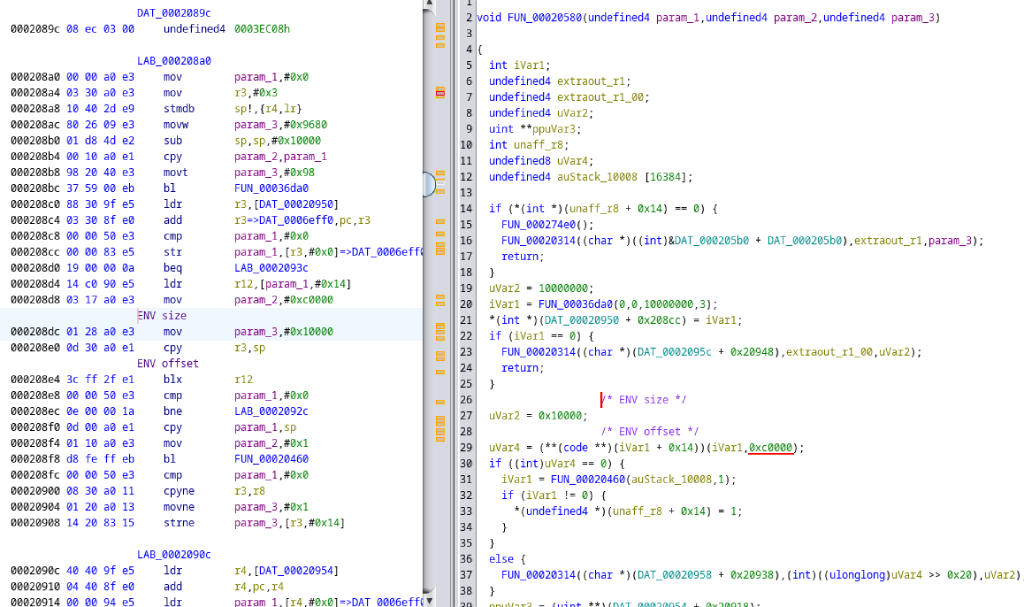
Ghidra disassembly of U-Boot binary showing environment read offset; Meraki have not provided the U-Boot source code for the MS410.
Networking is functional in U-Boot, so it is possible to boot arbitrary payloads via tftpboot.
Similar to the MS250, the two 40mm system fans in the MS410 are controlled by an onsemi adt7475 (PDF datasheet). The MS410 fans have a Meraki part number: MA-FAN-16K (P/N 680-36010) and contain the Delta FFB0412UHN-C (PDF datasheet). These are identical to the Cisco FAN-T1, which can be purchased for considerably less than the Meraki branded part.
The MS410 accepts two hot-swap power supplies (model MA-PWR-250WAC, P/N 640-20010), which in my units are Delta model DPS-250AB-86 with 12V/20.83A output. Note that the MA-PWR-250WAC is physically and electrically compatible with PWR-C2-250WAC. Higher wattage power supplies like the PWR-C2-640WAC and PWR-C2-1025WAC will also power the MS410.
Idle power consumption:
MS410-16: 35W
MS410-32: Unknown
Meraki have chosen to EoL all of their Broadcom based switches. Being a Broadcom design, the MS410 was axed from the product portfolio on 2024-09-28. The MS410 will continue to receive limited software support from Meraki until Q3 2029.
The GPL source code for the MS410 was requested from Meraki in March 2025, and at the time of writing Meraki has not provided any of the requested source code or an ETA on when they will comply.
| Model | Meraki Board | Part number |
|---|---|---|
| MS410-16 | Wolfcastle | 600-44010 |
| MS410-32 | Wolfcastle | 600-44020 |