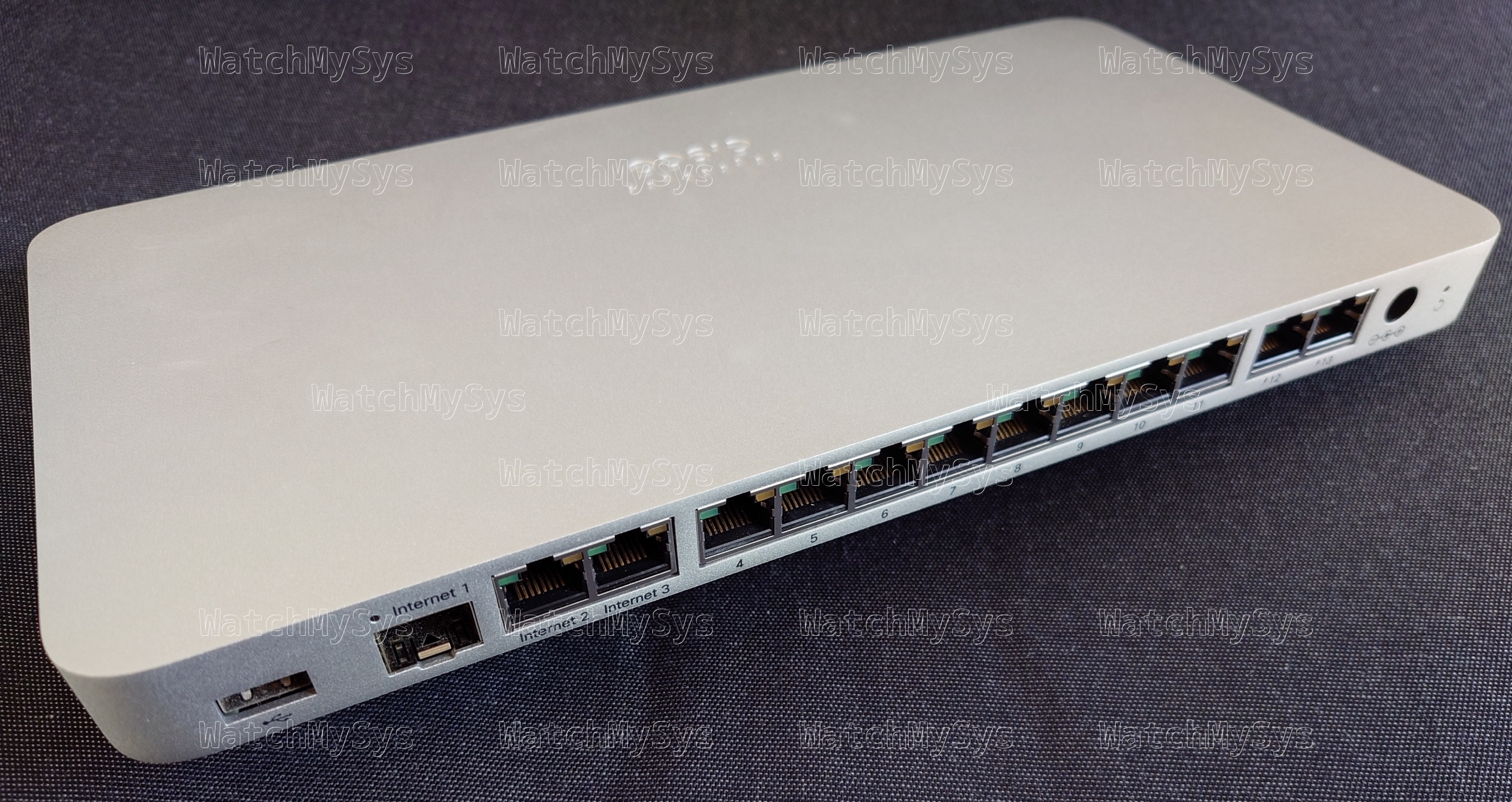
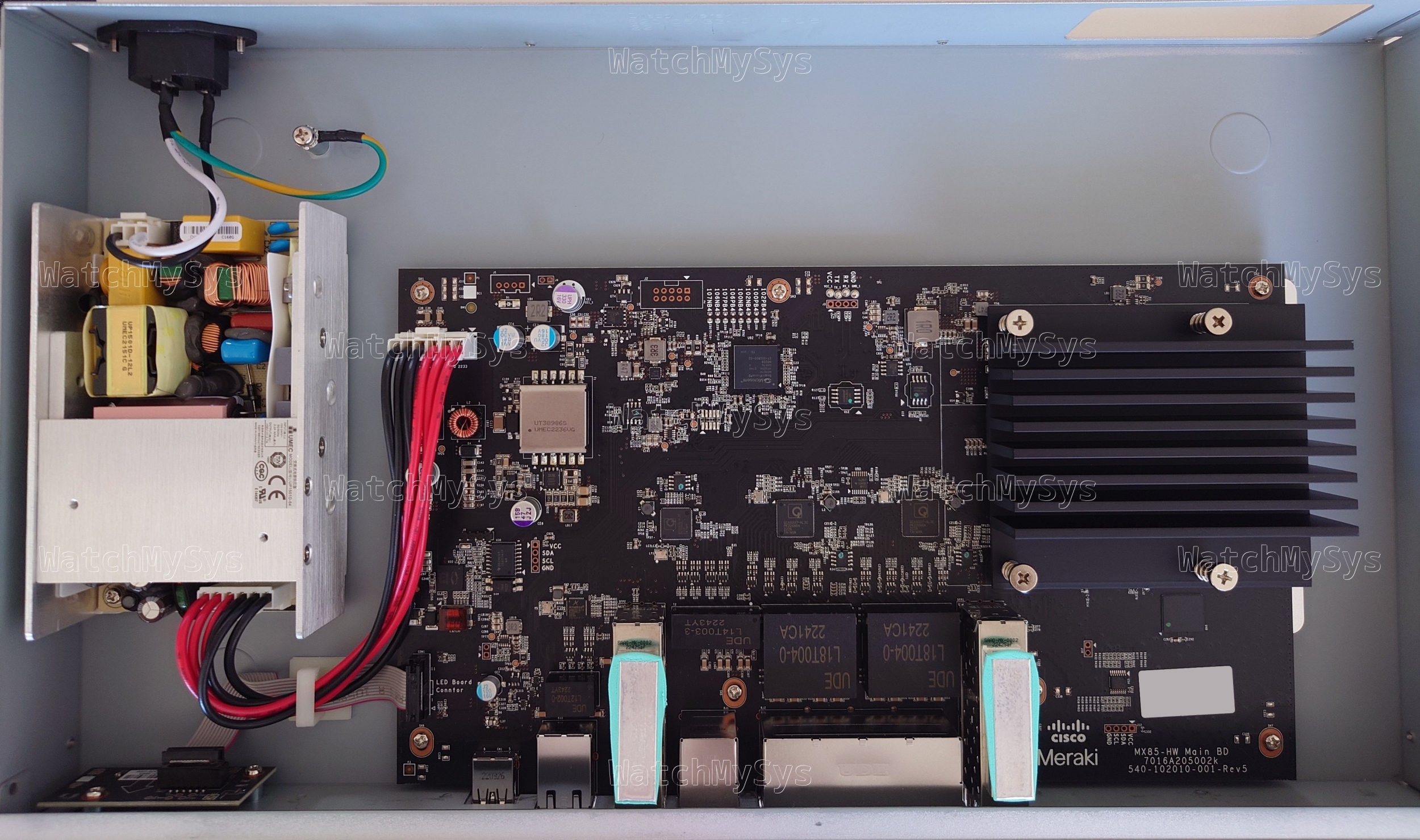
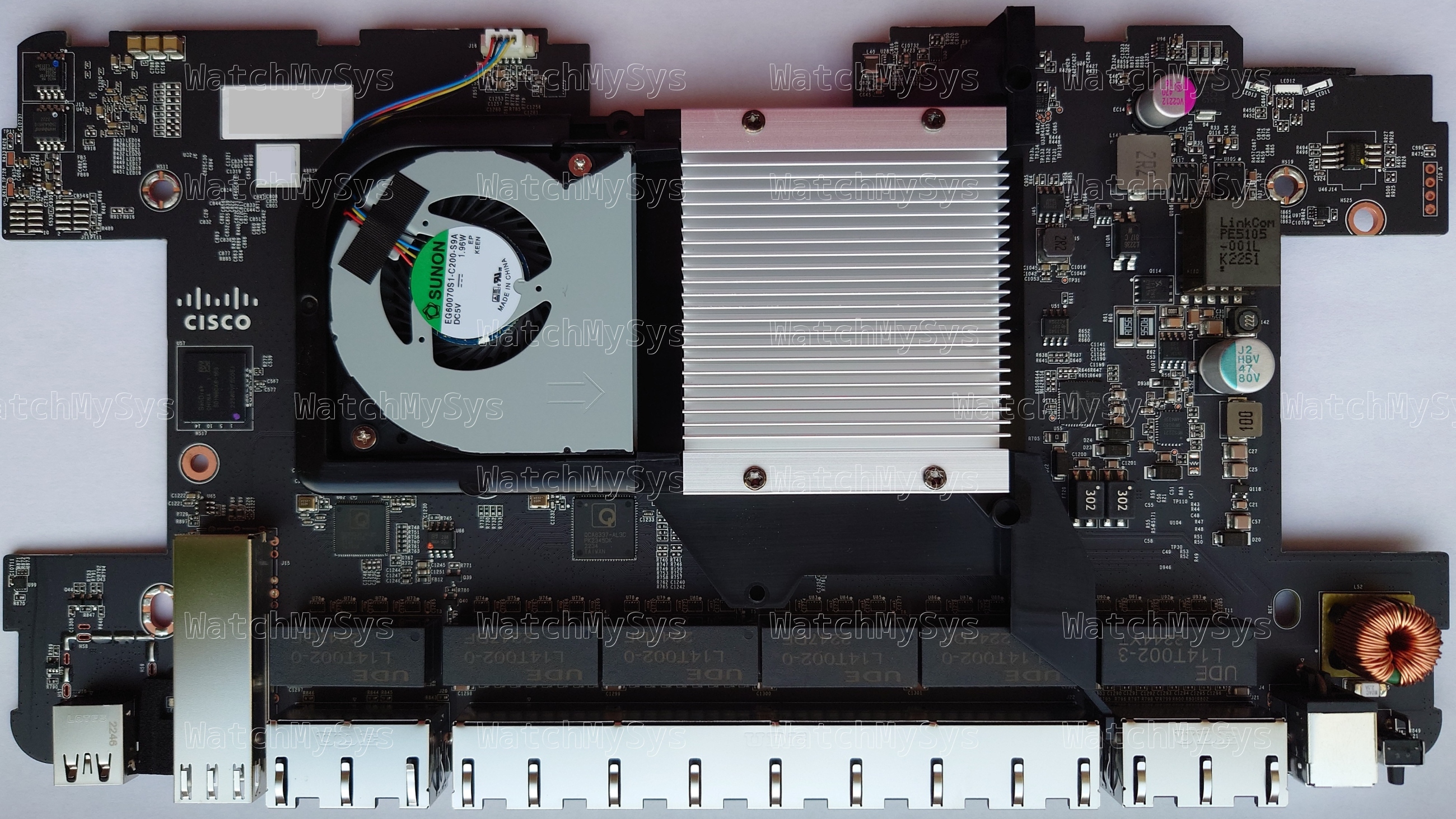
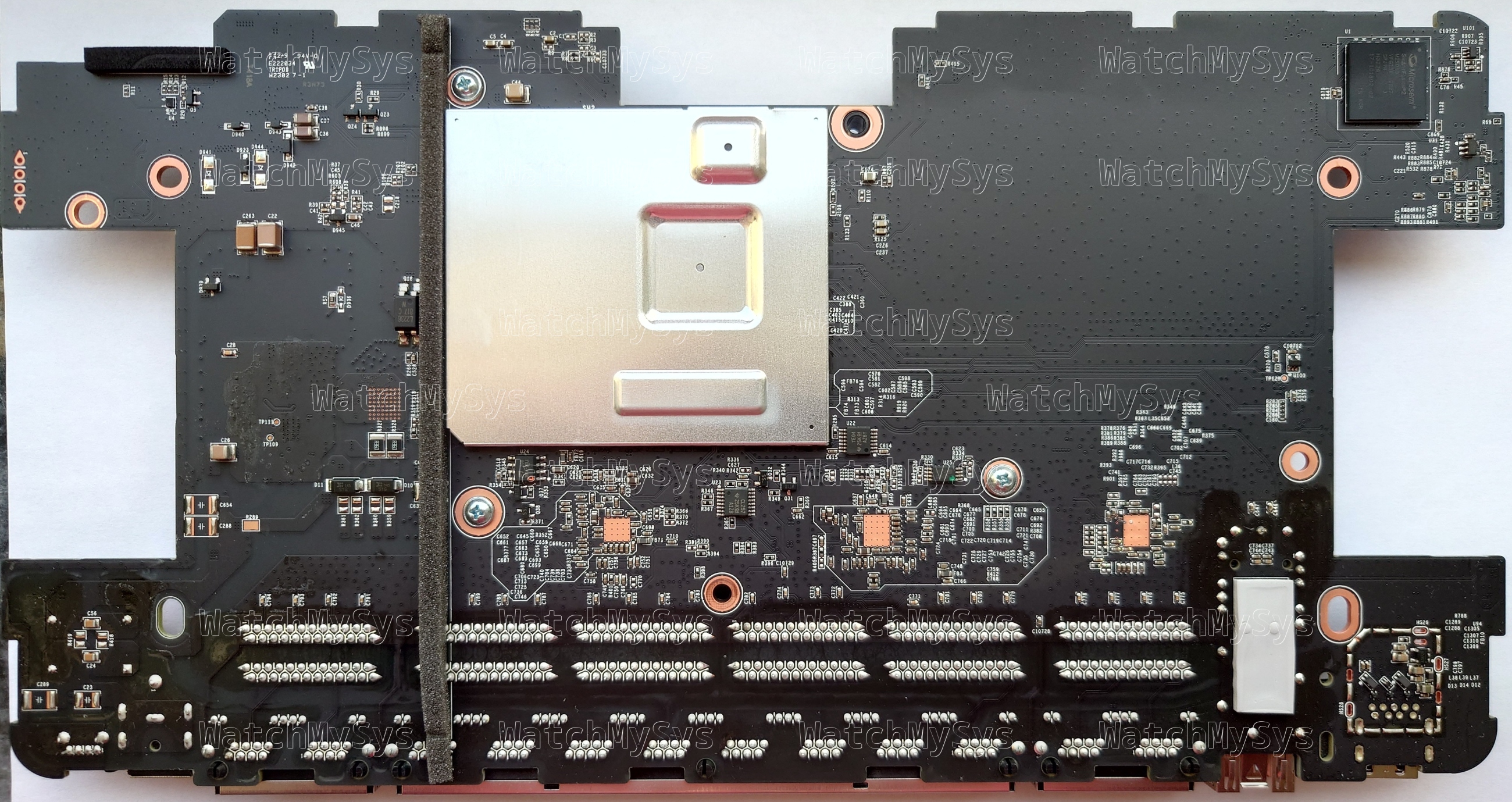
The Meraki MX75 SD-WAN appliance (codename “Barley Wine”) offers 3 WAN uplink ports (1 SFP, 2 Gigabit Ethernet), 10 LAN ports (8 Gigabit Ethernet, 2 PoE), and a USB 3.0 port for external cellular modems¹.
Here is a summary of the MX75 specs:
- NXP LayerScape LS1046A (ARM A72, 4 cores @ 1.8GHz)
- 4GB DDR4 RAM (Micron MT40A512M16LY-075:E running at 2100MT/s, 4 chips, soldered)
- 16GB of EMMC flash (SanDisk SDINBDA6-16G)
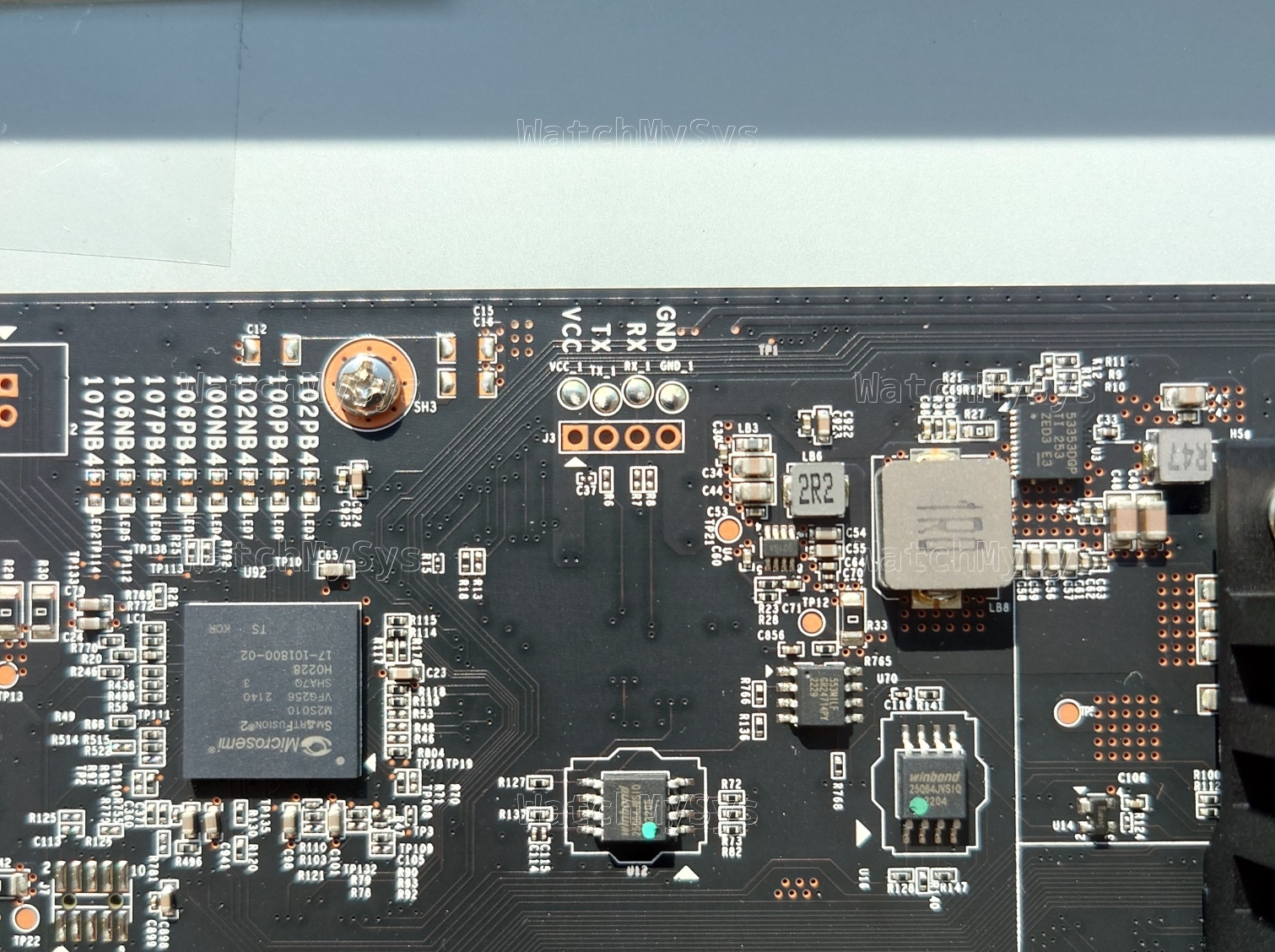
- Winbond W25Q64JVSIQ, MXIC MX25U6472F
- Aikido/Cisco TAM hardware root-of-trust (Microchip SmartFusion2 M2S010)
- Qualcomm QCA8337-AL3C 7-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (x2, PDF datasheet)
- Qualcomm QCA8334-AL3C 4-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (PDF datasheet)
- Microchip PD69104B1 PSE controller (PoE LAN ports)
- Sunon EG60070S1-C200-S9A fan
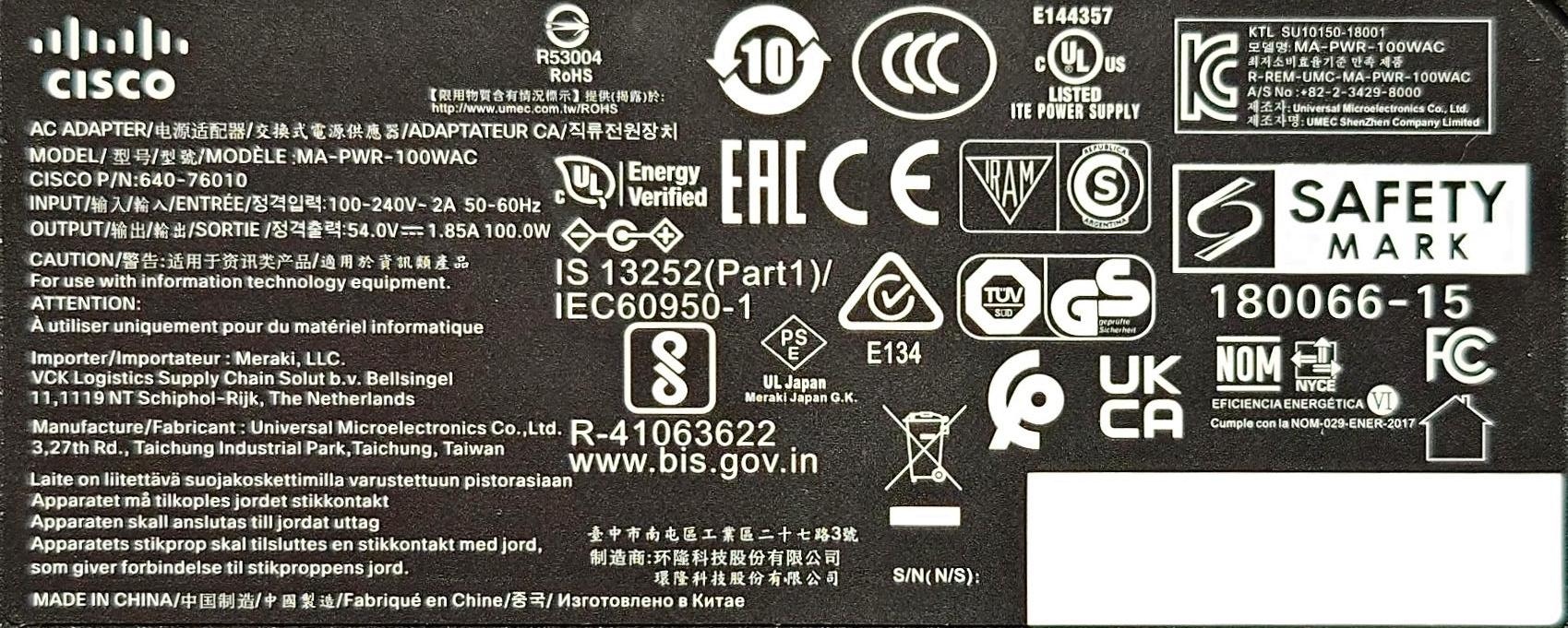
- UMEC 100W power supply (MA-PWR-100WAC)
Unlike the MX85, the MX75 has no dedicated management port.
The MX75 also does not support PoE output on any of the WAN ports; Meraki sales need some justification to upsell customers to an MX85! (Public service reminder that PoE injectors exist and are considerably less expensive than the cost difference from an MX75 to an MX85)
The MX75 uses the same LS1046A found in the passively cooled MX85, but has active cooling via a Sunon EG60070S1-C200-S9A fan. The thermal pad sales department definitely earned their quarterly bonus for this design win, because the MX75 has thermal pads above and below the metal EMI shield: 1.8mm (twice) for the memory and 1.2mm (twice) for the CPU. I offer this humble edit to the MX75 mounting instructions:
Please make sure there are no blockages or obstructions within one inch of the top of the chassis or within 0.5 inches of the sides so that nothing [except our overzealous use of thermal pads] interferes with cooling.
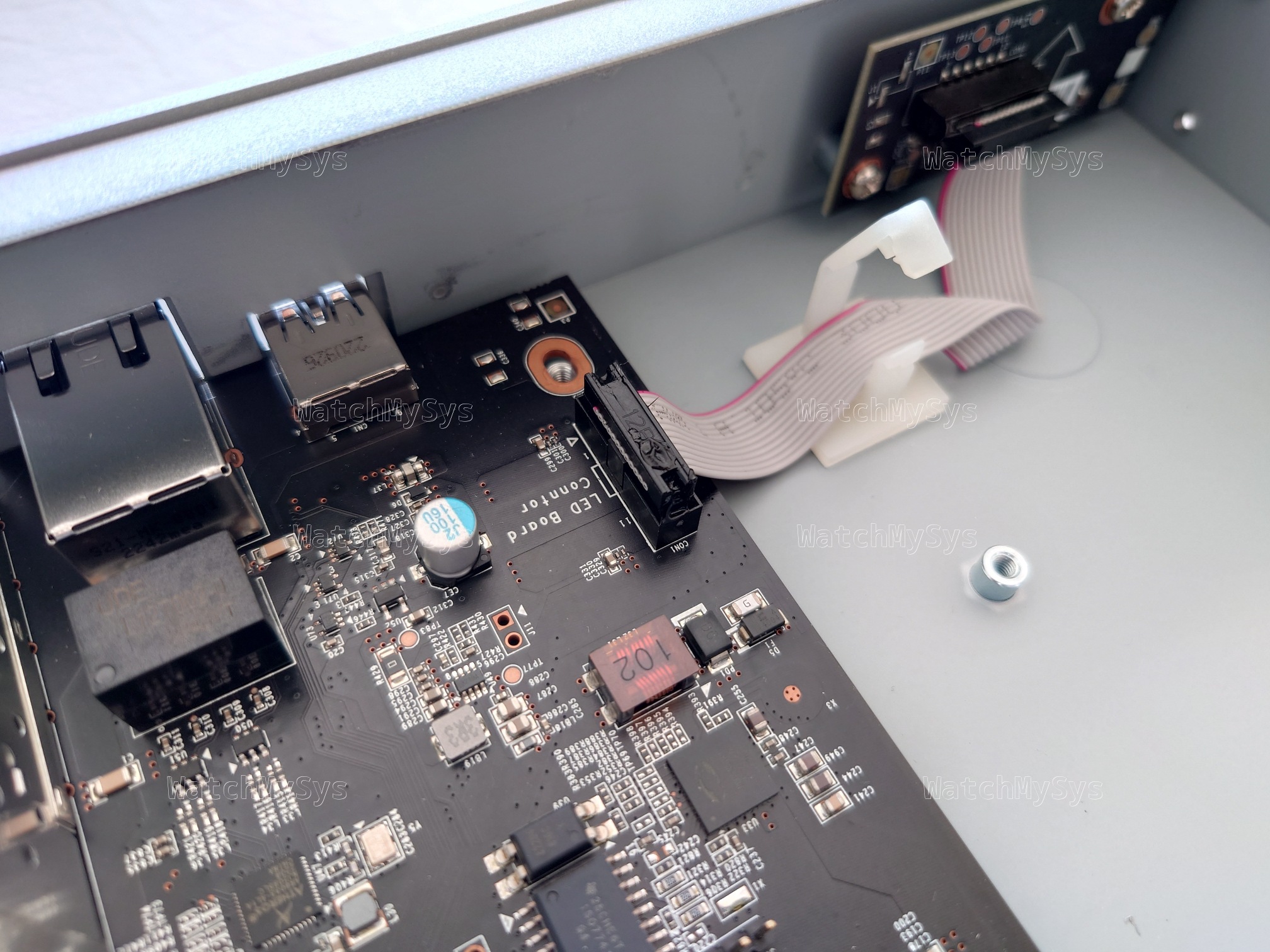
The UART header is J10 on the MX75 and follows the standard Meraki UART pinout (1: Vcc, 2: Tx, 3: Rx, 4: GND) at 3.3V and 115200 baud. Unlike the MX85 there are no resistors are missing, so just solder the 2.54mm header or use pogo pins.
The U-Boot release on the MX75 is 2018.09julia-spl-dandybar and, like all other recent Meraki products, it does not allow interrupting boot.
U-Boot SPL 2018.09julia-spl-dandybar (Mar 16 2021 - 00:27:48 +0000)
Initializing DDR....using SPD
Trying to boot from BOOTROM
U-Boot 2018.09julia-spl-dandybar (Mar 16 2021 - 00:27:48 +0000)
SoC: LS1046AE Rev1.0 (0x87070010)
Clock Configuration:
CPU0(A72):1800 MHz CPU1(A72):1800 MHz CPU2(A72):1800 MHz
CPU3(A72):1800 MHz
Bus: 700 MHz DDR: 2100 MT/s FMAN: 800 MHz
Reset Configuration Word (RCW):
00000000: 0e150012 10000000 00000000 00000000
00000010: 33330000 00b00012 40000000 c1000000
00000020: 00000000 00000000 00000000 00018ffc
00000030: 20004504 05003000 00000096 00000001
Model: LS1046A RDB Board
Board: LS1046ARDB, boot from Invalid setting of SW5
CPLD: V0.0
PCBA: V0.0
SERDES Reference Clocks:
SD1_CLK1 = 100.00MHZ, SD1_CLK2 = 100.00MHZ
I2C: ready
DRAM: Detected UDIMM Fixed DDR on board
3.9 GiB (DDR4, 64-bit, CL=15, ECC off)
SEC0: RNG instantiated
PPA Firmware: Version LSDK-18.09
GPIO: initialized
setting up RGB LED controller lp5562....
LM96163: initialized
Using SERDES1 Protocol: 13107 (0x3333)
Using SERDES2 Protocol: 0 (0x0)
SERDES2[PRTCL] = 0x0 is not valid
NAND: 0 MiB
MMC: FSL_SDHC: 0
EEPROM: meraki_MX75 600-103010
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Net: Invalid SerDes protocol 0x3333 for LS1046ARDB
Fman1: Uploading microcode version 108.4.9
Could not get PHY for MDIO1: addr 1
Failed to connect
Could not get PHY for MDIO2: addr 3
Failed to connect
Could not get PHY for MDIO2: addr 5
Failed to connect
PCIe0: pcie@3400000 disabled
PCIe1: pcie@3500000 disabled
PCIe2: pcie@3600000 disabled
FM1@DTSEC3 [PRIME], FM1@DTSEC5, FM1@DTSEC6, FM1@DTSEC9, FM1@DTSEC10
As we can see from the above ECC off output, the MX75 is using non-ECC RAM. This is similar to the MX65 which also did not include ECC memory. To my knowledge, no Meraki ARM-based designs incorporate ECC memory.
The MX75 also contains the Cisco TAM, implemented using a SmartFusion2 M2S010. The TAM is used for secure boot.
----Security Versions---- SecureBoot: R6.3.101-42a1499-20201106 SB Core: F01257R21.039b56e6b2020-06-29 Microloader: MK0007R01.0105062020 SF: Detected SPI Generic with page size 256 Bytes, erase size 4 KiB, total 16 MiB ----SecureBoot Registers---- system_invalid: 0 boot_check_count_error: 0 boot_done: 1 boot_ok: 1 boot_check_count_golden: 0 boot_check_count_upgrade: 2 boot_status_golden: 0 boot_status_upgrade: 1 first_bootloader: 1 ----Upgrade---- boot_error: 0 boot_check_count_error_vc: 0 boot_check_count_error: 0 boot_timeout_vc: 0 boot_timeout: 0 boot_cs_good: 1 boot_config_error: 0 boot_version_error: 0 boot_config_error_code: 0 boot_error_code: 0 boot_cs_good: 1 boot_version_error: 0 boot1_cs_key_type: 1 boot1_cs_return_code: 0 boot1_cs_key_index: 5 boot2_cs_return_code: 0 boot2_cs_key_index: 5 boot2_cs_key_type: 1 ----Other Registers---- fpga_version: 0090 Reading whitelist from TAM whitelist.bin: 744 bytes Converting whitelist to signature fdt BARLEY-WINE_LDWM-rel wired-arm64-OD-SECP384R1_1-rel wired-arm64-RT-SECP384R1_1-rel wired-arm64-AP-SECP384R1_1-rel wrote 558 bytes to 0000000082330000
Same story as the MX85, do not expect any OpenWrt support for this device.
Idle power consumption: ~15W
The MA-PWR-100WAC power supply (P/N: 640-76010) is manufactured by UMEC and outputs 54V @ 1.85A with a 6.5 x 3.0 mm center-positive barrel tip on a 175 cm long cable. It weighs 553g (without C13 cable) and has dimensions 170 x 70 x 40 mm.
The MA-PWR-100WAC power supply is physically larger and heavier than the MA-PWR-90WAC (427g, 153 x 65 x 36 mm) so it is more than an uprated version of the 90W power supply.
| Model | Codename | Part number |
|---|---|---|
| MX75 | Barley Wine | 600-103010 |
There are references to an MX75W in the firmware, however it appears this model was never publicly released. Certainly it would require a different PCB, as there are no unpopulated components on the MX75 PCB for a wireless radio or antennas.
The MX75 unit weighs 840g.
¹: USB modems with MX/Z series devices running firmware MX 18 or newer will be limited to best effort support and will not be receiving any future firmware fixes or improvements. Meraki documentation
It would seem that Meraki prefers their customers purchase an MG41 or MG51 than plug in their own USB LTE modem. Better margins and less to support, win-win!
The GPL source code for the MX75 was requested from Meraki in September 2024. At the time of writing Meraki has not provided any of the requested source code.