In this post, we’re going to discuss how you can configure the libvirt daemon to use TLS and SASL so that remote connections are encrypted. Please ensure that you have the appropriate packages for libvirt and gnutls installed before proceeding. certtool is part of the gnutls-bin package in Debian.
First we need to generate a CA certificate and key that will later be used to sign the server and client keys. If you already have a CA set up you can skip this step:
$ certtool --generate-privkey --sec-param=high > cakey.pem Generating a 3072 bit RSA private key... $ cat ca.info cn = mydomain.co ca cert_signing_key $ certtool --generate-self-signed --sec-param=high --load-privkey cakey.pem --template ca.info --outfile cacert.pem certtool --generate-self-signed --sec-param=high --load-privkey cakey.pem --template ca.info --outfile cacert.pem Generating a self signed certificate... X.509 Certificate Information: Version: 3 Serial Number (hex): 544bafeb011c172fe279cd4b Validity: Not Before: Sat Oct 25 14:12:59 UTC 2014 Not After: Sun Oct 25 14:12:59 UTC 2015 Subject: CN=example.com Subject Public Key Algorithm: RSA Algorithm Security Level: High (3072 bits) Modulus (bits 3072): 00:c0:72:2b:64:26:c4:76:dd:ab:b1:f7:67:67:22:f1 ff:31:03:b8:9d:9f:9e:c0:01:b9:db:de:50:f0:61:ff 0d:f5:ae:8a:96:e4:e6:75:a3:56:4d:41:7c:49:4c:6d 25:7f:de:b8:77:87:9d:c1:8b:4b:36:70:d4:a9:d9:c7 93:cb:a9:39:b1:73:29:b5:d9:5b:01:e2:60:57:f1:4b 42:a5:15:e8:e8:77:2b:3e:ec:4c:2a:0e:0f:0c:61:68 84:1e:09:9b:9d:7d:0a:87:97:24:07:a2:3d:06:c9:fa 91:cb:72:f1:61:01:a6:8b:6d:93:1f:dd:33:d9:1b:e9 3c:23:39:36:c2:a4:df:3c:44:d2:8e:b4:e4:20:37:11 36:7f:b7:9f:14:cd:d5:df:dc:16:fd:a8:a5:09:fa:ad cf:32:62:7e:0d:e2:af:80:f3:7a:bb:e9:d8:93:1d:6c f6:e2:4b:dd:2f:da:46:ce:fd:c7:41:95:9c:55:ee:66 a7:03:81:f9:8b:db:3b:03:a1:67:24:47:9a:25:3a:ba 30:77:34:4e:62:87:54:91:a6:09:09:a6:84:e4:93:76 09:b8:d3:5d:03:1b:2e:ea:aa:4a:6f:c3:99:1f:35:7d 74:0d:37:0f:a1:ae:82:6d:fc:5b:4f:b3:6d:5b:d3:f2 9f:65:fa:88:24:f9:2c:40:2a:88:72:23:80:7c:83:cb 95:2e:61:f2:38:3f:33:f9:08:4b:5f:72:ae:da:18:50 ed:d3:fd:22:9a:3e:3a:7d:f2:7e:c3:ea:f9:92:d0:62 3d:5c:15:98:a0:a8:96:0f:75:66:ed:72:48:56:42:46 c7:de:39:e3:9e:11:84:3d:bb:98:78:a1:33:c8:02:1d d3:c3:2e:93:fc:b9:16:bb:de:3d:3a:37:ee:1b:c6:7b 09:04:6e:5b:9d:2b:22:0e:ba:c4:b6:d2:29:f7:e1:fc 80:a3:ec:fb:ab:44:d9:fe:d4:4c:4c:cd:19:76:fc:4e 2f Exponent (bits 24): 01:00:01 Extensions: Basic Constraints (critical): Certificate Authority (CA): TRUE Key Usage (critical): Certificate signing. Subject Key Identifier (not critical): 51768ae1aea87f9bf1c60b103bc74db7b8b4480a Other Information: Public Key ID: 51768ae1aea87f9bf1c60b103bc74db7b8b4480a Public key's random art: +--[ RSA 3072]----+ | . o . | | . = o | | . = o | | + + + . | | E + + S . | | . B + o | | o =.o | | . .=o | | ....ooo. | +-----------------+ Signing certificate... # inspect the CA cert to ensure it was generated properly $ certtool -i --infile cacert.pem X.509 Certificate Information: Version: 3 Serial Number (hex): 544bafeb011c172fe279cd4b Issuer: CN=example.com Validity: Not Before: Sat Oct 25 14:12:59 UTC 2014 Not After: Sun Oct 25 14:12:59 UTC 2015 Subject: CN=example.com Subject Public Key Algorithm: RSA Algorithm Security Level: High (3072 bits) Modulus (bits 3072): 00:c0:72:2b:64:26:c4:76:dd:ab:b1:f7:67:67:22:f1 ff:31:03:b8:9d:9f:9e:c0:01:b9:db:de:50:f0:61:ff 0d:f5:ae:8a:96:e4:e6:75:a3:56:4d:41:7c:49:4c:6d 25:7f:de:b8:77:87:9d:c1:8b:4b:36:70:d4:a9:d9:c7 93:cb:a9:39:b1:73:29:b5:d9:5b:01:e2:60:57:f1:4b 42:a5:15:e8:e8:77:2b:3e:ec:4c:2a:0e:0f:0c:61:68 84:1e:09:9b:9d:7d:0a:87:97:24:07:a2:3d:06:c9:fa 91:cb:72:f1:61:01:a6:8b:6d:93:1f:dd:33:d9:1b:e9 3c:23:39:36:c2:a4:df:3c:44:d2:8e:b4:e4:20:37:11 36:7f:b7:9f:14:cd:d5:df:dc:16:fd:a8:a5:09:fa:ad cf:32:62:7e:0d:e2:af:80:f3:7a:bb:e9:d8:93:1d:6c f6:e2:4b:dd:2f:da:46:ce:fd:c7:41:95:9c:55:ee:66 a7:03:81:f9:8b:db:3b:03:a1:67:24:47:9a:25:3a:ba 30:77:34:4e:62:87:54:91:a6:09:09:a6:84:e4:93:76 09:b8:d3:5d:03:1b:2e:ea:aa:4a:6f:c3:99:1f:35:7d 74:0d:37:0f:a1:ae:82:6d:fc:5b:4f:b3:6d:5b:d3:f2 9f:65:fa:88:24:f9:2c:40:2a:88:72:23:80:7c:83:cb 95:2e:61:f2:38:3f:33:f9:08:4b:5f:72:ae:da:18:50 ed:d3:fd:22:9a:3e:3a:7d:f2:7e:c3:ea:f9:92:d0:62 3d:5c:15:98:a0:a8:96:0f:75:66:ed:72:48:56:42:46 c7:de:39:e3:9e:11:84:3d:bb:98:78:a1:33:c8:02:1d d3:c3:2e:93:fc:b9:16:bb:de:3d:3a:37:ee:1b:c6:7b 09:04:6e:5b:9d:2b:22:0e:ba:c4:b6:d2:29:f7:e1:fc 80:a3:ec:fb:ab:44:d9:fe:d4:4c:4c:cd:19:76:fc:4e 2f Exponent (bits 24): 01:00:01 Extensions: Basic Constraints (critical): Certificate Authority (CA): TRUE Key Usage (critical): Certificate signing. Subject Key Identifier (not critical): 51768ae1aea87f9bf1c60b103bc74db7b8b4480a Signature Algorithm: RSA-SHA256 Signature: 7f:f2:41:4a:1b:23:34:48:f0:1d:03:1d:ee:94:51:86 8f:5c:ff:c6:69:db:f3:8e:9a:be:5d:82:47:a3:e0:c2 1f:e4:eb:1d:3c:9f:63:a2:40:b4:6a:cd:dd:48:74:d1 03:67:b2:04:c5:27:30:04:75:5b:32:7f:ec:cb:c3:cc 3d:f8:d2:60:64:62:20:d5:29:a9:67:70:76:d4:34:a0 a1:fe:34:97:f4:42:7e:bc:67:0a:35:c8:c9:53:35:13 65:d2:4f:10:d3:ed:cd:6c:2f:3e:a9:0a:56:0f:48:5f 17:1c:4c:14:2b:c8:c5:77:01:d1:73:6c:08:45:d3:1c e2:24:46:53:f9:2a:7b:dd:fe:19:6c:8d:b0:17:ad:c3 f1:56:3c:dd:e7:da:02:57:3c:56:42:c8:1a:d7:59:e0 38:fb:f6:7a:ed:88:7b:e6:86:66:58:2c:ce:6a:d9:00 a8:2e:6b:f4:c1:61:a1:19:d2:d6:46:92:1c:84:2a:c6 85:34:56:c8:22:d9:cd:23:98:3f:33:7e:2a:f0:f4:e9 9a:f4:bf:dd:83:52:38:5f:cc:d3:5e:4b:c8:9f:61:7a c9:28:8b:39:b3:10:84:08:75:6b:1f:82:74:7f:b2:a8 7b:7c:50:0f:59:54:fc:b9:9e:f8:62:07:2d:1d:3d:9b 16:39:95:6e:4a:fb:c0:2b:a2:2e:7d:f1:fa:11:95:66 81:57:9c:33:be:19:e4:41:1b:31:39:1e:5f:e8:28:41 ef:0c:99:bc:e1:7a:6f:78:65:b2:c0:86:d2:2f:a7:81 85:58:ca:41:df:b3:b4:de:a2:fe:6f:ed:3e:6b:ad:b8 db:9c:f9:39:c1:e7:9e:c9:1e:47:11:b6:e7:f5:57:ae 25:eb:8d:ae:53:7d:9d:48:f5:a3:3a:7d:1b:7b:58:a1 32:ae:7e:bb:04:56:ca:e5:c6:40:c3:7d:cb:e0:be:cd c9:7f:10:66:bc:75:87:82:2c:c8:db:a4:11:c6:e3:24 Other Information: SHA1 fingerprint: 58ecea66161b1fdd4b292c83a631be8f870ceebd SHA256 fingerprint: 779ed901764da3ef9f6a4326dfb3067617e0d9c75ccadd3ea542a2e7c7ed8be6 Public Key ID: 51768ae1aea87f9bf1c60b103bc74db7b8b4480a Public key's random art: +--[ RSA 3072]----+ | . o . | | . = o | | . = o | | + + + . | | E + + S . | | . B + o | | o =.o | | . .=o | | ....ooo. | +-----------------+ -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIID+TCCAmGgAwIBAgIMVEuv6wEcFy/iec1LMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMBYxFDAS BgNVBAMTC2V4YW1wbGUuY29tMCIYDzIwMTQxMDI1MTQxMjU5WhgPMjAxNTEwMjUx NDEyNTlaMBYxFDASBgNVBAMTC2V4YW1wbGUuY29tMIIBojANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEF AAOCAY8AMIIBigKCAYEAwHIrZCbEdt2rsfdnZyLx/zEDuJ2fnsABudveUPBh/w31 roqW5OZ1o1ZNQXxJTG0lf964d4edwYtLNnDUqdnHk8upObFzKbXZWwHiYFfxS0Kl Fejodys+7EwqDg8MYWiEHgmbnX0Kh5ckB6I9Bsn6kcty8WEBpottkx/dM9kb6Twj OTbCpN88RNKOtOQgNxE2f7efFM3V39wW/ailCfqtzzJifg3ir4Dzervp2JMdbPbi S90v2kbO/cdBlZxV7manA4H5i9s7A6FnJEeaJTq6MHc0TmKHVJGmCQmmhOSTdgm4 010DGy7qqkpvw5kfNX10DTcPoa6CbfxbT7NtW9Pyn2X6iCT5LEAqiHIjgHyDy5Uu YfI4PzP5CEtfcq7aGFDt0/0imj46ffJ+w+r5ktBiPVwVmKColg91Zu1ySFZCRsfe OeOeEYQ9u5h4oTPIAh3Twy6T/LkWu949OjfuG8Z7CQRuW50rIg66xLbSKffh/ICj 7PurRNn+1ExMzRl2/E4vAgMBAAGjQzBBMA8GA1UdEwEB/wQFMAMBAf8wDwYDVR0P AQH/BAUDAwcEADAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUUXaK4a6of5vxxgsQO8dNt7i0SAowDQYJKoZI hvcNAQELBQADggGBAH/yQUobIzRI8B0DHe6UUYaPXP/Gadvzjpq+XYJHo+DCH+Tr HTyfY6JAtGrN3Uh00QNnsgTFJzAEdVsyf+zLw8w9+NJgZGIg1SmpZ3B21DSgof40 l/RCfrxnCjXIyVM1E2XSTxDT7c1sLz6pClYPSF8XHEwUK8jFdwHRc2wIRdMc4iRG U/kqe93+GWyNsBetw/FWPN3n2gJXPFZCyBrXWeA4+/Z67Yh75oZmWCzOatkAqC5r 9MFhoRnS1kaSHIQqxoU0Vsgi2c0jmD8zfirw9Oma9L/dg1I4X8zTXkvIn2F6ySiL ObMQhAh1ax+CdH+yqHt8UA9ZVPy5nvhiBy0dPZsWOZVuSvvAK6IuffH6EZVmgVec M74Z5EEbMTkeX+goQe8Mmbzhem94ZbLAhtIvp4GFWMpB37O03qL+b+0+a62425z5 OcHnnskeRxG25/VXriXrja5TfZ1I9aM6fRt7WKEyrn67BFbK5cZAw33L4L7NyX8Q Zrx1h4IsyNukEcbjJA== -----END CERTIFICATE-----
Now that we have a CA certificate and signing key we need to generate a server key for the libvirt host:
$ certtool --generate-privkey --sec-param=high > serverkey.pem Generating a 3072 bit RSA private key... $ cat libvirt_server.info organization = example.com cn = libvirt.example.com tls_www_server encryption_key signing_key $ certtool --generate-certificate --sec-param=high --load-privkey serverkey.pem --load-ca-certificate cacert.pem --load-ca-privkey cakey.pem --template libvirt_server.info --outfile servercert.pem Generating a signed certificate... X.509 Certificate Information: Version: 3 Serial Number (hex): 544bb10a049f2eaca4b04d94 Validity: Not Before: Sat Oct 25 14:17:46 UTC 2014 Not After: Sun Oct 25 14:17:46 UTC 2015 Subject: CN=libvirt.example.com,O=example.com Subject Public Key Algorithm: RSA Algorithm Security Level: High (3072 bits) Modulus (bits 3072): 00:eb:77:a6:12:6f:a5:a6:b1:aa:9b:b2:fa:aa:38:48 52:9c:4f:5b:ae:0b:2f:08:71:6e:6e:25:21:88:d2:3a eb:16:08:98:70:ee:30:2b:bb:11:42:c8:c7:e8:f9:eb f3:c6:1e:b5:76:2b:dd:c3:5f:63:10:87:33:45:bd:f3 ac:7b:a0:da:bd:05:8e:fa:75:0f:de:27:b8:1a:23:d4 86:ba:0a:52:11:8a:55:83:e1:6c:68:2e:b5:74:10:1d 21:35:14:d8:6f:11:14:67:59:f9:b3:db:fc:9a:5b:3c 5d:91:bb:d2:30:74:a6:45:99:e1:a2:f4:5d:e9:a1:bd 68:fc:ba:63:3c:91:95:cd:5d:99:f0:75:8c:ac:26:9a 70:44:47:ae:e7:70:95:b8:25:b2:fd:42:99:bf:74:a1 54:e4:4f:14:ae:05:3b:d7:5d:85:c6:d8:5a:72:aa:28 8c:a4:c5:0d:bb:86:44:d2:b0:9c:c8:c9:c9:a5:ab:c2 1b:dd:b9:73:dd:ac:f7:9e:d0:4a:9a:fa:c0:ea:bb:8c 07:93:80:64:12:08:78:ff:50:37:3b:3f:e1:ee:5b:89 c6:47:fd:f6:7d:80:6f:e4:1a:7c:5e:62:c0:36:dc:eb 6c:66:85:50:3d:f7:1b:e0:9f:5f:9b:62:a3:d7:1a:4c 8f:3b:b1:4f:a7:f0:9f:95:ef:ac:ac:58:aa:db:e1:fb 75:64:7a:77:c3:59:61:56:65:9d:d7:c6:51:be:70:48 ae:b3:c1:98:b5:7e:12:b7:59:8e:76:90:e1:de:48:b7 ce:1f:15:82:cc:85:1e:08:ba:66:4b:14:ce:f4:bd:a8 60:21:f0:21:66:a1:6d:a9:38:ec:8e:a4:67:43:ef:a5 64:8d:14:7d:93:8f:28:85:6a:41:b2:e1:b6:62:19:1b 1f:5a:b1:6a:85:bf:b7:1a:31:3c:c7:25:a8:43:ee:6f 94:0c:43:0c:9b:a8:81:7d:77:50:0a:d5:fb:f0:52:b4 fd Exponent (bits 24): 01:00:01 Extensions: Basic Constraints (critical): Certificate Authority (CA): FALSE Key Purpose (not critical): TLS WWW Server. Key Usage (critical): Digital signature. Key encipherment. Subject Key Identifier (not critical): 83d19f1391ea516d2d499f7c94ac1c9703b44cd7 Authority Key Identifier (not critical): 51768ae1aea87f9bf1c60b103bc74db7b8b4480a Other Information: Public Key ID: 83d19f1391ea516d2d499f7c94ac1c9703b44cd7 Public key's random art: +--[ RSA 3072]----+ | .+o*o.=| | . o.B++OE| | . .o...+B o| | oo. o o . | | ..S.+ | | .. . | | | | | | | +-----------------+ Signing certificate... $ certtool --generate-privkey --sec-param=high > clientkey.pem Generating a 3072 bit RSA private key... $ cat client1.info country = DE organization = example.com cn = client1.example.com tls_www_client encryption_key signing_key $ certtool --generate-certificate --sec-param=high --load-privkey clientkey.pem --load-ca-certificate cacert.pem --load-ca-privkey cakey.pem --template client1.info --outfile client1cert.pem Generating a signed certificate... X.509 Certificate Information: Version: 3 Serial Number (hex): 544bb184075bcf2e62d42003 Validity: Not Before: Sat Oct 25 14:19:48 UTC 2014 Not After: Sun Oct 25 14:19:48 UTC 2015 Subject: CN=client1.example.com,O=example.com,C=DE Subject Public Key Algorithm: RSA Algorithm Security Level: High (3072 bits) Modulus (bits 3072): 00:bb:c4:26:e1:ab:bf:ea:bc:db:b2:88:c0:6e:9a:d4 a6:97:fc:cc:3a:8e:ae:49:69:80:35:86:0f:2d:a6:36 e9:ac:8e:7a:04:bd:d9:4c:0f:85:d7:80:bf:5e:26:37 38:40:20:03:9a:c2:49:ed:a1:4f:42:9e:be:28:12:a8 00:42:6c:6e:7d:08:0d:b8:bf:72:ef:2b:2e:a6:68:40 df:ec:97:00:75:48:f6:96:03:a9:46:71:2b:db:99:3a ab:28:00:01:09:60:be:7d:a3:cd:0c:44:b9:99:35:91 04:3d:96:48:9b:26:06:ca:4f:3f:18:84:37:84:8b:8a b1:fd:9b:5f:00:b7:89:b6:f7:32:75:1b:cb:33:12:cc b0:ff:b6:05:58:08:df:54:24:da:73:4e:fd:6f:e7:2b 59:16:5e:a7:7b:1b:86:ee:38:02:73:09:bd:a8:73:60 eb:7f:87:12:c6:fe:b8:c4:c3:e4:ea:85:c4:43:94:5c dc:a3:ca:73:4a:08:0d:0a:8a:de:51:c7:c1:bf:f3:39 91:54:cc:44:00:9c:a8:bc:0a:de:e3:20:63:04:dc:e8 c3:52:0c:0e:34:43:8a:00:0a:19:07:d0:63:cf:c4:a3 4e:01:52:7f:33:89:24:47:9d:e1:3d:75:5c:76:2f:f0 91:21:ce:cd:9a:97:64:03:2e:6b:4f:31:27:cf:d2:8c 83:83:83:82:5b:76:a4:b7:7a:43:da:d7:40:32:69:aa 04:27:1b:40:91:04:df:ce:35:b2:d7:f6:24:9f:3b:3c f4:c6:f8:33:80:e3:43:c7:b0:dc:d5:42:f9:fb:0c:df d7:04:44:24:47:49:ca:d2:13:19:91:fa:48:31:92:4f 5a:73:86:02:78:3c:25:75:32:f3:24:7d:e3:c6:57:68 62:f2:a9:76:d5:81:5b:50:64:27:42:a2:6d:1e:e7:b6 79:85:f9:31:18:33:74:08:78:91:90:e2:fe:9d:97:42 73 Exponent (bits 24): 01:00:01 Extensions: Basic Constraints (critical): Certificate Authority (CA): FALSE Key Purpose (not critical): TLS WWW Client. Key Usage (critical): Digital signature. Key encipherment. Subject Key Identifier (not critical): 77f16cb983bae8ee1e205e5f60340bb5793af951 Authority Key Identifier (not critical): 51768ae1aea87f9bf1c60b103bc74db7b8b4480a Other Information: Public Key ID: 77f16cb983bae8ee1e205e5f60340bb5793af951 Public key's random art: +--[ RSA 3072]----+ | ..+ | | o = | | * . E | | . = . + . | | . o S + . = | | . o o = o o . | | . o . . o | | o . . | | =* o. | +-----------------+ Signing certificate...
We’ve just created a CA certificate and signing key, a certificate and key for the libvirt server, and a client certificate/key pair for a client (e.g. a laptop).
Now we need to install the certificates in the appropriate places:
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/CA /etc/pki/libvirt/private $ sudo cp cacert.pem /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem $ sudo chmod 0644 /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem $ sudo cp servercert.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/servercert.pem $ sudo chmod 0644 /etc/pki/libvirt/servercert.pem $ sudo cp serverkey.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/private/serverkey.pem $ sudo chmod 0600 /etc/pki/libvirt/private/serverkey.pem
Edit the libvirt configuration to listen for TLS connections and use SASL for authentication:
$ sudo vi /etc/libvirt/libvirtd.conf # Override the default configuration which binds to all network # interfaces. This can be a numeric IPv4/6 address, or hostname # listen_addr = "10.0.0.10" auth_tls = "sasl"
On Debian you need to edit the libvirt daemon configuration to enable listening, otherwise libvirt will only accept local connection attempts:
$ sudo vi /etc/default/libvirt-bin # options passed to libvirtd, add "-l" to listen on tcp libvirtd_opts="-l"
Configure SASL to handle the authentication for libvirt:
$ sudo cat /etc/sasl2/libvirt.conf # If you want to use the non-TLS socket, then you *must* include # the GSSAPI or DIGEST-MD5 mechanisms, because they are the only # ones that can offer session encryption as well as authentication. # # If you're only using TLS, then you can turn on any mechanisms # you like for authentication, because TLS provides the encryption # # Default to a simple username+password mechanism mech_list: digest-md5 # Before you can use GSSAPI, you need a service principle on the # KDC server for libvirt, and that to be exported to the keytab # file listed below #mech_list: gssapi # # You can also list many mechanisms at once, then the user can choose # by adding '?auth=sasl.gssapi' to their libvirt URI, eg # qemu+tcp://hostname/system?auth=sasl.gssapi #mech_list: digest-md5 gssapi # Some older builds of MIT kerberos on Linux ignore this option & # instead need KRB5_KTNAME env var. # For modern Linux, and other OS, this should be sufficient # # There is no default value here, uncomment if you need this #keytab: /etc/libvirt/krb5.tab # If using digest-md5 for username/passwds, then this is the file # containing the passwds. Use 'saslpasswd2 -a libvirt [username]' # to add entries, and 'sasldblistusers2 -f [sasldb_path]' to browse it sasldb_path: /etc/libvirt/passwd.db
Now add the users you want to authenticate with libvirt to the SASL database for the libvirt daemon:
$ sudo saslpasswd2 -a libvirt hmartin Password: Again (for verification): $ sudo sasldblistusers2 -f /etc/libvirt/passwd.db hmartin@libvirt: userPassword
Now restart the libvirt daemon to apply the changes:
$ sudo service libvirt-bin restart
Verify that libvirt is listening for incoming connections:
$ sudo netstat -anp | grep libvirt tcp 0 0 10.0.0.10:16509 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 12565/libvirtd tcp 0 0 10.0.0.10:16514 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 12565/libvirtd
Copy the CA certificate, client certificate, and client key to the computer you’ll be using to connect to libvirt, and then install them similar to how we installed the certificates and key on the server:
$ scp cacert.pem client1cert.pem clientkey.pem client1.example.com: client1 $ sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/CA /etc/pki/libvirt/private client1 $ cp cacert.pem /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem client1 $ sudo chmod 0644 /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem client1 $ cp client1cert.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/clientcert.pem client1 $ sudo chmod 0644 /etc/pki/libvirt/client1cert.pem client1 $ cp clientkey.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/private/clientkey.pem client1 $ sudo chmod 0600 /etc/pki/libvirt/private/clientkey.pem
Inside virt-manager you need to add a new connection. Select “Connect to remote host” with the method “SSL/TLS with certificates”
Leave the username blank, and specify the FQDN of your server running libvirt (e.g. “libvirt.example.com”) and click “Connect”
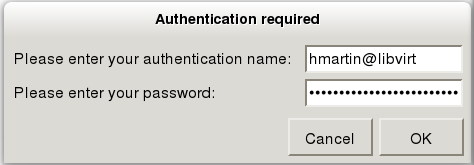
If virt-manager can successfully communicate with the libvirt daemon on the remote host, a dialog prompting you for your SASL username and password will appear:
Enter your username@hostname, for me this is “hmartin@libvirt”, and your user password in the credentials window that appears.
If you get an error when trying to connect to the remote host then I suggest reviewing the syslog and auth log on the remote host. Googling the python error from virt-manager can also help to determine what the issue is.
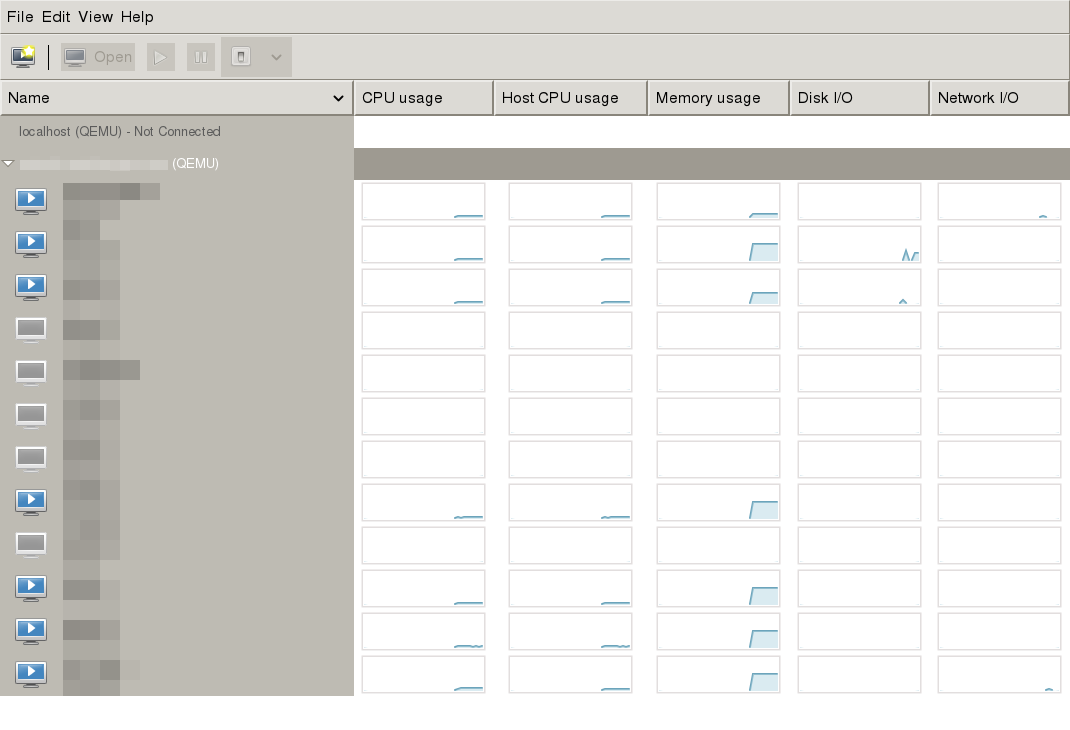
If you connected successfully to the libvirt host then you are now communicating with the libvirt daemon over a secure connection.
Not every interaction with your guests is encrypted with this configuration. The guest console is still unencrypted. If you are concerned about people eavesdropping on the console session you can restrict access by interface in the guest definition file, or configure TLS for the guest’s spice server, but I won’t cover those right now.